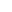
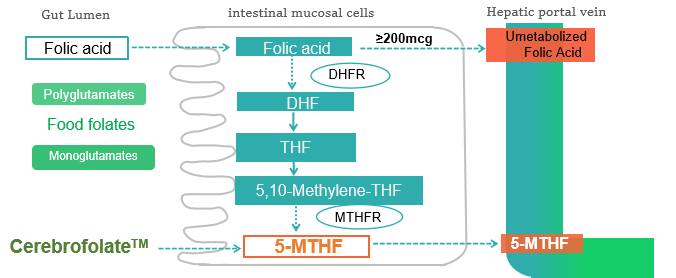
5-MTHF makes up to 95%~98% of total folate in blood. CerebrofolateTM is Calcium salt of L-5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid (or L-methylfolate (5-MTFH)) that contains a methyl group and is a reduced form of folate compared to the oxidized form of folic acid. It’s more bio-available than folic acid.
Factory Supply industrial standard L-methylfolate 151533-22-1 In Stock
- Molecular Formula:C20H23CaN7O6
- Molecular Weight:497.52
- Appearance/Colour:Off-white to pale yellow solid
- Melting Point:>300 °C
- PSA:208.43000
- LogP:-1.67900
Levomefolate calcium(Cas 151533-22-1) Usage
|
Function
|
Folic acid from Levomefolate calcium(Calcium L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate) will reduce the ability of cells to synthesize and repair DNA. Supplementing folic acid may be a more advantageous way to increase folic acid to reduce homocysteine levels, and support normal cell proliferation, vascular endothelial function. Cardiovascular disease, nervous system function, Especially supplementing 5-MTHF(Calcium L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate) during pregnancy has been shown to reduce the risk of neural tube malformations and recurrence.
|
|
Metabolic pathways
|
Ordinary folic acid must be converted to L- methylfolate to participate in the two main metabolic pathways: methylation process and DNA synthesis. The only form of free folic acid that usually appears in human plasma and cells is 5-mthf. Lack of folic acid is usually due to lack of vitamins, which leads to insufficient intake. During pregnancy, breastfeeding, and children's growth, the need for folic acid is increased.
|
|
Mechanism of Action
|
The? biochemical pathways of folic acid involves a series of enzymatic reactions and cofactors. The absorbed folic acid is reduced and methylated to 5-MTHF(Calcium L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate) during the metabolism of intestinal mucosal cells. This transformation is limited and does not change the appearance of folic acid in the blood circulation. The heavy amino acid is then converted to s-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), and the methyl donor is involved in a number of biochemical processes. It can also be used as a donor to participate in the synthesis of nucleotides and support biosynthesis of DNA.
|
|
Pharmacokinetics
|
Absorption: Orally administered levomefolate calcium is absorbed rapidly and is incorporated into the body folate pool. Peak plasma concentrations of about 50 nmol/l above baseline are reached within 0,5 to 1,5 hours after single oral administration of 0,451 mg levomefolate calcium.Distribution: Biphasic kinetics is reported for folates with a fast- and a slow-turnover pool. The fast-turnover pool probably reflecting newly absorbed folate is consistent with the terminal half-life of approximately 4 to 5 hours after single oral administration of 0,451 mg levomefolate calcium. The slow-turnover pool reflecting turnover of folate polyglutamate has a mean residence time of greater than or equal to 100 days. Exogenous folate and an enterohepatic folate cycle help to maintain a constant supply of L-5-methyl-THF. Elimination: L-5-methyl-THF is eliminated from the body by urinary excretion of intact folates and catabolic products as well as faecal excretion through a biphasic kinetics process. A rapid decline in urinary and faecal concentration of folates and their catabolites with a half-life of several hours is followed by a long decline with a half-life of about 100 to 360 days. Steady-state conditions: Steady-state conditions for L-5-methyl-THF in plasma after intake of 0,451 mg levomefolate calcium are reached after about 8 to 16 weeks depending on the baseline levels. In red blood cells achievement of steady-state is delayed due to the long life-span of red blood cells of about 120 days.https://www.bayer.com/sites/default/files/YASMIN_PLUS_EN_PI.pdf
|
|
Folic Acid Supplement
|
Folic acid is the man-made form of folate. Folate is a B-vitamin naturally found in some foods. It is needed to form healthy cells, especially red blood cells. Folic acid supplements may come in different forms (such as L-methylfolate, levomefolate, methyltetrahydrofolate). They are used to treat or prevent low folate levels. Low folate levels can lead to certain types of anemia. Conditions that can cause low folate levels include poor diet, pregnancy, alcoholism, liver disease, certain stomach/intestinal problems, kidney dialysis, among others. Women of childbearing age should receive adequate amounts of folic acid either through their diet or supplements to prevent infant spinal cord birth defects. The calcium salt of Levomefolate calcium which belongs to the group of folate vitamins (Vitamin B9, Folacin). It is a coenzymated form of folic acid and a more bioavailable alternative in dietary supplements.
|
|
Biological Functions
|
L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate calcium is the calcium salt of L-5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid, and a member of the folate group of vitamins (Vitamin B9). It is the coenzymated and most active form of folic acid, which performs many vital cellular functions, including DNA reproduction, cysteine cycle and homocysteine regulation. L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate calcium is used as in dietary supplements and has been proposed for treatment of cardiovascular disease.
|
InChI:InChI=1/C20H25N7O6.Ca/c1-27-12(9-23-16-15(27)18(31)26-20(21)25-16)8-22-11-4-2-10(3-5-11)17(30)24-13(19(32)33)6-7-14(28)29;/h2-5,12-13,22H,6-9H2,1H3,(H,24,30)(H,28,29)(H,32,33)(H4,21,23,25,26,31);/q;+2/p-2/t12-,13-;/m0./s1
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego